Gertu tools
The information provided below constitute a source of information which may turn out useful when selecting appropriate tools for a given type of work.
Screwdrivers and blades
A screwdriver is one of the simplest manual tools. Depending on the application, screwdrivers have different blade types.
Common blade types:
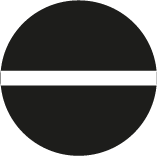
Slotted
It is characterized by a flat blade. It is marked with S or SL.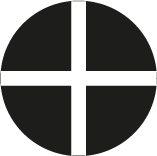
Phillips
The tip features a cross shaped incision with pointed edges and the same cross incision in the screw head. It is marked with PH or Ph.
Pozidriv
The tip features a cross shaped incision with parallel edges and the same cross shaped incision in the screw head. It is marked with PZ or Pz.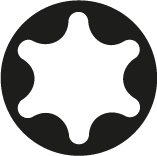
Torx
It is characterized by an incision in the shape of a 6-point star. It is marked with a T.
External Torx
It is characterized by a groove in the shape of a 6-point star. It is marked with a T.
Torx TS
It is characterized by an incision in the shape of a 6-point star with a slot inside, as an additional protection against unauthorized manipulation.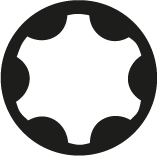
Torx Plus
It shows increased drive system strength in comparison to the conventional Torx to minimize the wear. It is not compatible with standard Torx screws.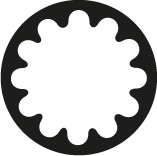
XZN (Triple square)
It has a blade with twelve evenly distributed incisions. The structure enables high drive system strength.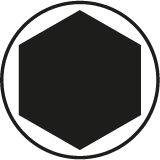
External hexagon
It is shaped like a hexagon.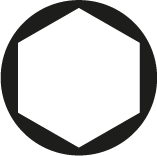
Hexagon
internal (Imbus) - it is shaped like a hexagon.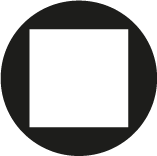
Square (Robertson)
The tip is shaped like a square.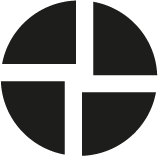
Torq-Set
It is characterized by a cross shaped incision whose lines are displaced in relation to each other.
Tri-Wing
The screws feature three incisions at 120 degrees angle which makes it similar to a three point star.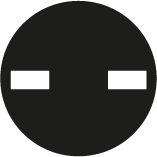
Spanner
It features two incisions situated opposite each other. It prevents unauthorized manipulation.Rockwell hardness scale
The hardness of metals is determined according to a Rockwell test which consists in measuring the depth of penetration of a model 120O diamond cone on a tested material using appropriate load.
The hardness of metal is marked as HR+ depending on the type of alloy:
- C and A - hardened steel,
- B and F - unhardened steel and non-ferrous metals,
- N and T - used when the specimen is small sized or very thin.
When indicating the reading according to Rockwell scale, the symbol includes the mark which reflects the method, e.g. HRC for C method. The range of the Rockwell scale starts at 20 for soft alloys to 100 for hardened steel (the hardest steel - martensite - shows hardness of 65-70 HRC).
Hammers
A hammer is one of the most frequently used tools. It is used to deliver an impact to an object with the aim of its treatment, to deliver an impact to other tool (chisel, punch etc.) or to drive fasteners (nails, keys) in a given surface.
Structure
A hammer consists of two basic elements: a head and a handle.
The head is usually made of tool steel but in case of specific-purpose hammers the head can be made of rubber or some type of wood.
The shape of the head is usually an elongated cuboid with a cut end on one or both sides.
The handle can be made of wood, plastic, sometimes tool steel.
The connection between the head and the handle is sometimes reinforced by a key.
Types of hammers
Apart from a typical hammer used for mechanical works, there are the following types of hammers for special purposes:
- dressing hammer - rubber. It is made of hard rubber, flexible plastic or tool steel finished with rubber face. It is mainly used to shape metal sheets, but can be used in stonemasonry as well. The principal benefit of this hammer is the fact that it does not damage varnished surfaces which makes it suitable for shaping varnished surfaces during repairs.
- claw hammer - with a characteristic structure where one of the claws is longer than the other. The head may feature a magnetic slot which holds nails.
- shoemakers’ hammer - it has a rounded off head which is suitable for driving nails into soft surfaces and prevents the damage of the shoe leather. The other side of the head may feature claws for pulling out nails.
- brick hammer - its characteristic feature is its high weight. It is used to break bricks, crush stone etc. Apart from its slightly bigger size, it has a standard structure.
- geologist’s hammer - geologist’s hammer : its structure and field of use are similar to that of the brick hammer. It has a flat and a sharp end of the head which enables splitting rocks.
- carpenter’s hammer - its head is made of hardwood. It is used to strike other tools, hammer pegs etc.
- welding hammer - it is used to remove slag from welds.
- stone mason hammer - it has a flat-ended head. It can be used to lay setts etc.
Pliers
A hand tool used for manual works. Pliers feature a pair of metal levers joined in a similar manner to scissors. They are usually made of tool steel coated with a plastic on the handle.
Pliers are used to handle, bend, squeeze objects or to remove insulation from electrical wires. The jaws of the pliers are flat and feature a rough gripping surface which ensures that the objects held do not slip out.
The handles are coated with insulating plastic or wood.
The pliers may feature side cutters for cutting wires.
Types of pliers
Depending on the structure, there are the following types of pliers:
- flat pliers
- long nose pliers
- diagonal pliers
- round pliers
- push pin pliers
- lock pliers
- others.
Files
A file is a tool used to cut amounts of material from 0.01mm to 1-2mm from a workpiece. They are made of steel, sometimes it is a hardened steel. It consists of a face and tang to which a handle can be fitted.
The face features a series of teeth which are tilted to one or two sides, frequently in a diagonal manner in relation to the axis of the file.
Depending on their application, files differ in size and shape of the bar, and the size and shape of teeth.
Files can have various profiles: triangular, stripes, oval, round, square, half round etc.
Depending on the field of use, various numbers of teeth are applied. There are the following types of files (in ascending order of the number of teeth):
- coarse files
- bastard cut files
- second cut files
- smooth files
- dual smooth files
- dead smooth files
Files are suitable for the treatment of a wide range of materials: wood, metal, plastics. They are used by craftsmen and workers from many industries.
Saws
A saw is an independent or incorporated into other machine tool which has a toothed edge for cutting any material (most frequently wood, metals, plastics, stone etc.) by forceful movements of the toothed edge against the material. In case of manual saws this force is applied by hand.
Saws consist of a blade - toothed edge stretched on a long bow or featuring one or two handles at the ends which are used to move the saw. The teeth of the saw are usually wedged, curved or square.
Manual saws can be divided into:
- Frame saws (e.g.: bow saw, ripping saw, tenon saw, turning saw)
- Frameless saws (e.g.: panel saw, back saw, keyhole saw, fine saw)
- Crosscut saws (double-handled, bow saw, garden saw etc)
Tool steel
Efficient tools have to be made of hard steel resistant to abrasion, deformations and overheating. The addition of alloying elements, such as chromium, wolfram or molybdenum, and adequate thermal treatment ensure that these requirements are met.
Tool steel is an ideal material for the production of tools which are used to shape and cut materials in a temperature of up to 600°C and for the production of measuring devices used in ambient temperature.
Carbon tool steel
Tools made of conventional tool steel (carbon) are used for works in temperature of up to 200°C. Such steel is manufactured as high quality killed in nine grades of C percent of 0.55% to 1.35% and in two variations:
- Shallow hardening (N7E – N13E),
- Deep hardening (N5 – N13).
Tools made of tool steel cut at low speed. The use of deep hardened tool steels is not limited while the use of shallow hardened steel is limited to tools with a section thinner than 20mm.
Application and hardness of selected carbon tool steels:
| Grade | %C | HRC hardness level | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| N5* | 0.55 | 58 | Hammers, axes, ironworker tools, gripping parts of tools made of alloy steels. |
| N8E, N8* | 0.8 | 61 | Pneumatic tools, for the treatment of soft stone and wood, snips blades, dies. |
| N11E, N11* | 1.1 | 62 | Drills, cutters, reamers, taps, thread rolling tools, nail making tools, lathe centres, disc cutters, dies. |
| N13E, N13* | 1.3 | 63 | Tools for slow cutting, hacksaws, scrapers, files, engraving tools, straight razors, draw plates, dies. |
Alloy tool steel
Alloy tool steel is used for both: hot and cold work. Tools made of alloy tool steel are designed to be used in the temperature range of 200 – 250°C.
The principal ingredient of the steel is chromium (Cr), optionally with an addition of wolfram (W), vanadium (V) or molybdenum (Mo).
Steels with a medium content of carbon (0.4% to 0.6%) are used in the production of tools exposed to dynamic loads. High carbon steels (above 0.75%) are used in the production of tools exposed to high dead load and slow cutting tools.
Chemical composition and application of selected tools intended for cold work:
| Group | Grade | Average chemical composition % | Application | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Mn | Si | Cr | W | V | |||
| I | NZ2* | 0,45 | 0,30 | 0,95 | 1,05 | 1,90 | 0,22 | Pneumatic tools, chisels, rivet heads, punches. |
| II | NC5* | 1,37 | 0,30 | 0,27 | 0,55 | - | - | Surgical instruments, engraving tools, straight razors, files, glass cutting wheels. |
| III | NMWV | 0,95 | 1,15 | 0,27 | 0,55 | 0,55 | 0,17 | Measuring tools, hacksaws, dies. |
| IV | NC11* | 1,95 | 0,30 | 0,27 | 12,0 | - | - | Highly efficient cutting tools, deep drawing tools, forming rolls and flange rolls. |
The application of tool steel for hot work are tools exposed to temperatures of up to 600°C exposed to high dead and dynamic loads.
Such steel is mainly used for the production of tools for hot forming processes at risk of abrasion and tempering of high temperatures. Thus, it should be as hard as possible and retain its hardness in the temperature at which the tool is used. When working under dynamic loads it should demonstrate sufficient ductility of 0.3 – 0.6%C (carbon).
Chemical composition and application of selected tools intended for hot work:
| Group | Grade | Average chemical composition % | Application | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Mn | Si | Cr | Mo | V | inne | |||
| I | WWV* | 0,30 | 0,37 | 0,27 | 2,75 | - | 0,4 | 9,0W | Dies under high loads, pressure casting forms, draw plates for hot work. |
| WCL* | 0,38 | 0,35 | 1,00 | 5,00 | 1,35 | 0,4 | - | Pressure casting forms, die inserts. | |
| II | WNL* | 0,55 | 0,65 | 0,27 | 0,65 | 0,20 | - | 1,6Ni | Forming dies, anvil, punches, die inserts. |
| WLK* | 0,35 | 0,37 | 0,45 | 2,75 | 2,75 | 0,5 | 3,0Co | Punches for high-speed machines. | |
High speed steels
High speed steel is intended for cutting materials at a high speed. It can be used without the loss of hardness in temperatures of 550 – 600°C. As a result of the addition of a significant amount of alloying elements of up to 30%, the steel has high resistance to tempering.
Chemical composition and hardness of selected high speed steels:
| Grade | Average chemical composition % | HRC hardness after hardening and tempering | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Cr | W | V | Mo | Co | ||
| SW18* | 0,8 | 4,0 | 18,0 | 1,2 | - | - | 64 |
| SW2M5* | 0,95 | 4,0 | 1,8 | 1,3 | 5,0 | - | 64 |
| SK5M* | 0,9 | 4,0 | 6,4 | 1,9 | 4,9 | 5,0 | 65 |
| SK10V* | 1,2 | 4,0 | 10,0 | 3,0 | 3,3 | 10,0 | 66 |
Applicable standards
EN10020
Definitions and classification of grades of steel.
The standard gives a definition of “steel” and provides a classification of the grades of steel according to their chemical composition into carbon steels, corrosion resistant steels and other alloy steels and a division into quality classes.
EN10027-1
Steel grade designation system. Symbols.
The standard contains a description of marking system of steels which contains letter and numerical symbols which indicate the application and features of a given steel, e.g. mechanical properties, physical properties, chemical composition, which makes it easy to identify particular types of steel.
The standard specifies the application of steels listed in European Standards (EN), Technical Specifications (TS), Technical Reports (TR) and national standards of CEN member states. The rules can be applied to steels not included in the standards.
EN10027-2
Steel grade designation system. Numbers.
The standard specifies the European marking system of steels which includes marks and numbers of steels. The system is limited to steels, however, its scope can be broadened to other industrial materials.
The numbers of steels have a fixed number of digits which makes the processing of data easier in comparison to the system which involves the use of symbols. The standard provides guidelines as to the determination of number codes, their registration and distribution.
In accordance with the classification of steels, two-digit numbers have been given to the groups of steels. The standard contains application forms for the determination of numbers for grades which are classified based on their chemical composition and mechanical properties.
GS certificate

Certificate for household appliances, lighting, manual electric tools, office equipment and IT devices intended for the German market.