Protective footwear most often is intended for the protection against several kinds of dangers at the same time. The basic task of the protective footwear is the protection of feet and legs from mechanical or chemical damage and also burns, harmful influence of low and high temperatures as well as wetness.
Protective characteristics depend most of all on the materials used in production of footwear as well as the construction and the possible accessories, such as puncture resistant insoles, ankle protections etc.
Providing adequate legs protection has a crucial impact on the safety and comfort of a worker moving in a workplace.
List of standards
Parts of the shoe
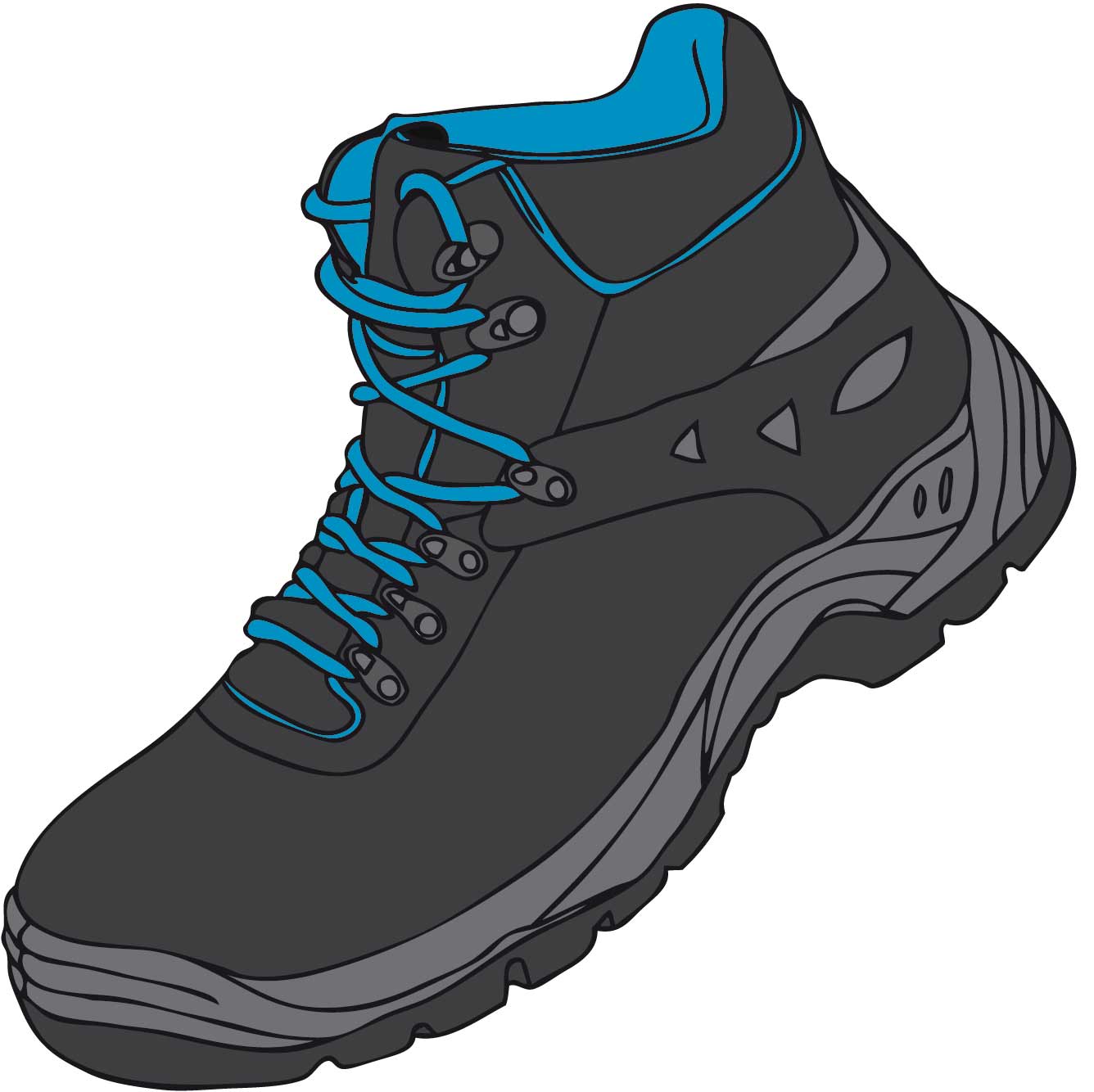

| A TongueB ShaftC LiningD Toe protectionE SoleF Lug sole | G Puncture resistant insoleH Under-soleJ Heel protectionK Sole excessL Ankle protectionM Upper |
EN13287
Personal protective equipment. Footwear. Test method for slip resistance.
The standard defines the test methods for slip resistance of safety, protective and professional footwear with typical soles. The range covered by the standard does not include the footwear for special purpose equipped with spikes, metal studs or other similar elements.
EN14404
Personal protective equipment. Knee protectors for work in kneeling position.
The standard states the requirements for knee protectors intended for work in kneeling position. It defines the requirements concerning marking of the knee protectors and the information that shall be provided by the manufacturer.
It describes the test methods and defines the levels of protection effectiveness. In case, when protection against additional dangers is declared, the requirements of protection effectiveness given in other standards can also be applied. The range covered by the standard does not include the knee protectors, which are medical products or are intended for sports purposes.
EN20344
Personal protective equipment. Footwear test methods.
The standard defines test methods for the footwear intended for personal protection. It also defines the requirements concerning the whole footwear, upper, lining, tongue, under-sole and sole.
This standard can be applied only in close connection with the EN20345, EN20346 and EN20347 standards, which specify the requirements in relation to footwear depending on the levels of specific dangers that occur.
Each type of safety footwear has to be marked indelibly and clearly - by stamping or hot marking, which include the following information : size, footwear number, type mark according to the manufacturer, manufacturer’s logo, date of production (quarter and year), reference to the numbers of European standard, appropriate symbol(s) indicating protective characteristics or (if it applies) appropriate category (SB, S1...S5).
Markings that may appear on footwear:
| A | antielectrostatic footwear |
| AN | ankle protection |
| C | conductive footwear |
| CI | bottom insulation from cold |
| CR | upper resistance against cutting |
| E | energy absorption in the heel part |
| ESD | electric resistance between 0,75 - 35 MOhm |
| FO | sole resistance to diesel oil |
| HI | bottom insulation from heat |
| HRO | sole resistance to contact with hot floor up to 300 (±5)°C |
| M | metatarsus protection |
| P | bottom resistance to the puncture force of 1100 N |
| SRA | Slip resistance on ceramic tile floor with sodium lauryl sulphate (NaLS) solution |
| SRB | resistance on steel floor with glycerol |
| SRC | slip resistance on both abovementioned floors (SRA+SRB) |
| WR | water resistance of the whole footwear |
| WRU | resistance of the upper to water penetration and absorption |
| Antistatic | anti electrostatic properties |
As far as the fire service footwear is concerned, applied marking has to be in accordance with the following list:
| F | High footwear for fire fighters, |
| FP | High footwear for fire fighters with puncture resistant sole, |
| FA | High footwear for fire fighters with anti electrostatic properties, |
| FAP | High footwear for fire fighters with anti electrostatic properties, puncture resistant sole. |
In case of resistance against cutting by hand chainsaws, the resistance classes are defined as 0, 1, 2 and 3.
Insulating protector is defined by a class 00,1,2,3,4.
The requirements defined in these standards can be divided into three categories:
- SB or S1 to S5 (safety footwear),
- PB or P1 to P5 (protective footwear),
- O1 to O5 (professional footwear).
Shoes made of any material which are classified to SB category (defined by EN20345 standard) and PB (EN20346 standard) have basic protective properties.
Categories of the safe footwear with the most frequently used combination of the requirements of the EN ISO 20345:2011*:
| SB | Basic properties (i.a. toe reinforcement resistant to striking with 200 J and crushing up to 15 kN) |
| S1 | Basic properties + Closed heel area + Anti-electrostatic properties + Energy absorption under the heel part + sole resistance to diesel oil. |
| S2 | as for S1 + Resistance of the upper part to water permeability and absorption. |
| S3 | as for S2 + Resistance of the bottom to punching/piercing + Sole modelling. |
| S4 | Basic properties + Closed heel area + Anti-electrostatic properties + Strikes absorption under the heel + sole resistance to diesel oil. |
| S5 | as for S4 + resistance of the bottom to punching/piercing + sole modelling. |
| SBH | designation for the category of a hybrid safety footwear |
Special professional footwear categories with the most frequently used combination of the requirements of EN ISO 20347:2012 standard:
| OB | Basic properties. |
| O1 | Basic properties + Closed heel area + Anti-electrostatic properties + Energy absorption under the heel part. |
| O2 | as for O1 + Resistance of the upper part to water permeability and absorption. |
| O3 | as for O2 + Resistance of the bottom to punching / piercing + sole modelling. |
| O4 | Basic properties + Closed heel area + Anti-electrostatic properties + Energy absorption under the heel part. |
| O5 | as for O4 + Resistance of the bottom to punching/piercing + sole modelling. |
| OBH | designation for the category of a hybrid safety footwear |
EN20345
Personal protective equipment. Safety footwear.
The standard defines, with regard to EN20344 standard, the basic and additional requirements for the safety footwear for work, marked with the letter „S”.
The footwear defined by the standard has to be equipped with a safety toecap which protects against impact at the maximum energy level of 200 J and against compression force of 15 kN.
Details of the division of the footwear included in this specification are placed in the description of the EN20344 standard.
EN20346
Personal protective equipment. Protective footwear.
The standard, with regard to the EN20344 standard, defines the basic and additional requirements for the protective footwear for work, marked with the letter “P”. The footwear defined by the standard has to be equipped with a safety toecap which protects against impact at the maximum energy level of 100 J and against compression force of 10 kN.
Details of the division of the footwear included in this specification are placed in the description of the EN20344 standard.
EN20347
Personal protective equipment. Professional footwear.
The standard, with regard to the EN20344 standard, defines the basic and additional requirements for the professional footwear for work, marked with symbol “O”. This footwear differs from the safety footwear in that it is not equipped with safety toecaps protecting from impacts and compressions.
Details of the division of the footwear included in this specification are placed in the description of the EN20344 standard.
EN61340-4-3
Static electricity. Standardised test methods for specific applications - Footwear.
In the standard, there is described the method of specifying the electric resistance of the footwear used for protecting against static charge build-up in a human body. The method is intended to be used by the manufacturers as well as the footwear users. The described method of measuring the electric resistance of the footwear alone is designed as the acceptance testing of new footwear. The insulating footwear is not included in the range - despite the fact that the given technique of resistance measurement can be applied to it.
EN61340-5-1
Static electricity. Protection of electronic devices against static electricity. Basic requirements.
The standard defines the administrative and technical requirements indispensable for creating, implementing and maintaining program of the static electricity protection. It covers the following areas: manufacturing, processing, assembling, installing, packaging, labelling, exploitation, testing, control and other activities connected with the use of electric and electronic elements, units and devices susceptible to damage by electrostatic discharges greater than or equal to 100 V human body model. It does not apply to electrically initiated explosive devices, flammable liquids, gases and powders.
EN381-3

Protective clothing for portable chainsaw users. Footwear test method.
The standard defines the test methods for the footwear resistance against chainsaw cut.
Test methods for the chainsaw cut resistance of other kinds of feet and legs protection (e.g. gaiters) are defined in other standards.
The range of the standard covers only the footwear with integrated protection against cut.
EN381-5

| Resistance class | Chain speed |
|---|---|
| 0 | 16m/s |
| 1 | 20m/s |
| 2 | 24m/s |
| 3 | 28m/s |
Protective clothing for portable chainsaw users. Requirements concerning leg protectors.
The standard belongs to the standards concerning personal protective equipment intended for protection against dangers occurring while using hand chainsaws.
NOTE: No protection measures can provide 100% protection against cut by hand chainsaw. Nonetheless, the tests have shown that it is possible to produce the protection measures which provide protection to a certain level.
- A - class of resistance against cut at the chain speed (0-3)
- X - type of anti cut surface (A,B,C)
The range of the leg protectors is defined by three letters A,B,C defining the surface of the material covering the anti cut unit.
EN17249
Safety footwear resistant to chainsaw cut.
The requirements concerning the safety footwear resistant to chainsaw cut are provided. The classification, requirements, marking and the information attached are explained.
The standard should be applied together with EN20345, EN20344 and 381-3 standards.
The standard excludes certain shaft models (only the models marked with the letters C, D and E are acceptable and the required minimal height of the shaft in the C model has been risen up). Additionally, the necessity of equipping the footwear with the safety toecaps has been defined.
The meaning of the icons used on the footwear
Icons symbolising footwear parts
 | Sole. It is a reference to the shoe sole for determining the material of which it is made. |
 | Padding. It is a reference to the material of which the inner part of the shoe is made for determining its kind. |
 | Upper part. It is a reference to the upper of the footwear for determining the material of which it is made. |
Icons of the material, of which footwear elements are made
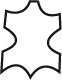 | Leather | 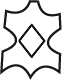 | Coated leather |
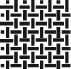 | Textiles | 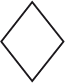 | Other materials, including plastics. |
ESD footwear

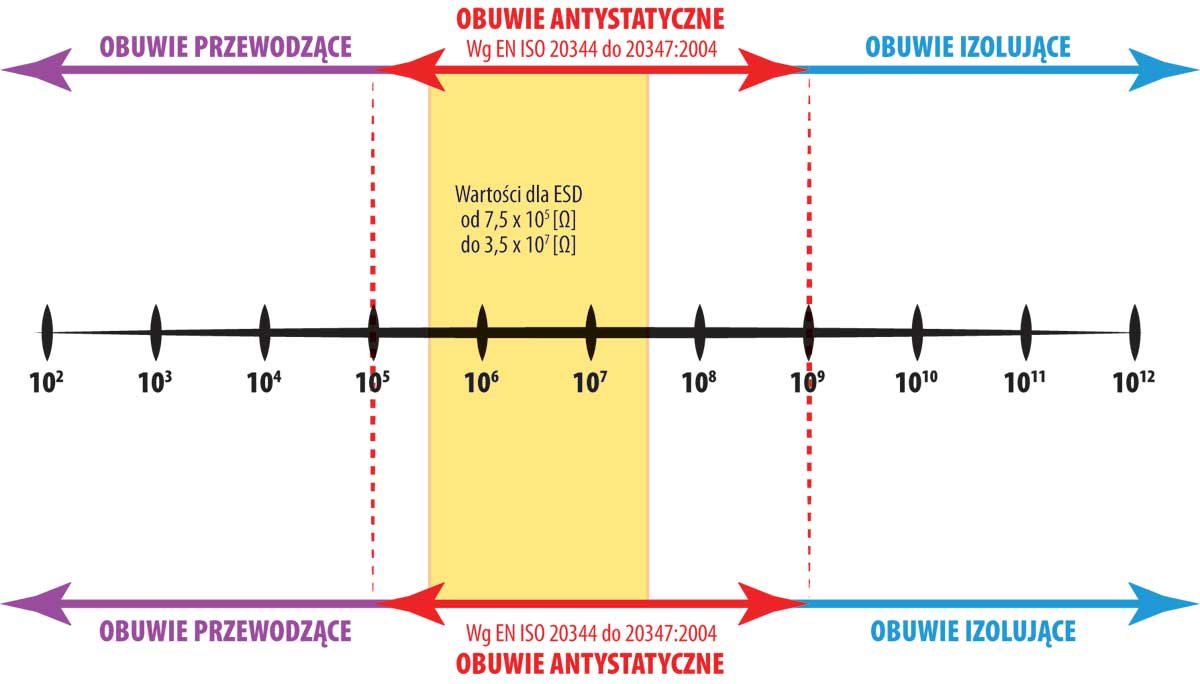
Static electricity is a common, polysemic term for electrostatic charge as well as the phenomena of its creation, accumulation and dissipation.
A specific form of electrostatic charge dissipation are electrostatic discharges (ESD) - short electric impulses appearing in the space between objects of sufficiently big difference of electrostatic potentials, which lead to full or partial dissipation of the electrostatic charge from those objects.
Because the discharges last relatively short time, from several dozens of nanoseconds to several hundreds of microseconds, created impulses are very strong, enough to ignite explosive atmospheres, shock workers, damage solid state devices. Electrostatic dangers are understood as potential possibility of occurrence of the abovementioned electrostatic discharge effects.
The use of inserts
| A Disparities of lower limbsB HalluxC Lopsided fingersD Varus fingersE Hammer toes | F Longitudinal platypodiaG Transverse platypodiaH Heel spursI Lopsided heel |
The effects of electrostatic charge build-ups are especially severely felt in winter, in unconditioned, centrally heated rooms, when the relative air humidity, in extreme conditions, fall down to a dozen or so percent. Such conditions, as the result of a significant increase of material electric resistance, reinforce the creation of electrostatic charges and maintaining the state of electrostatic charge build-up by a particular material or object. Among others, inappropriately chosen personal protective equipment has a large influence on the level of the danger occurring in the work environment. On the one side, it can inadequately protect human from external impact of static electricity, and on the other side, it may cause dangerous electrostatic charge build-up of the human body.*
The footwear protecting from the ESD effect allows to prevent electric charge build-up of a person wearing footwear e.g. as the effect of friction while walking on certain surfaces, thus it prevents dangerous electrostatic discharges. On the other hand, if electrostatic discharge happens or a worker has a contact with high voltage, it is thanks to the resistance of minimum 0,75 MΩ that the results are mitigated.
ESD footwear should be used when there is a necessity to prevent electrostatic charge build-up of a worker by discharging static electricity. The presence of the factors such as climate, dirt, material properties, surface resistance, shoe design either aggravates or enhances the properties of ESD shoe.
Stopy

Feet are a very important part of human body. The specialists confirm that there are about 7000 receptors, which are responsible for particular body organs, placed on feet. This is why healthy feet are so important for overall health and well-being.
Deformed feet can cause spinal problems and even changes in knee or hip joints. Feet ailments can also be the reason of an inappropriate gait, which in the effect can have a bad impact on the health of the internal organs in the pelvis area.
An effective way to take care of the feet on daily basis is using appropriate insoles.
Socks
Systems used in socks to provide comfort of use

1 Protect System
terry zone, which occurs in the construction of many models of socks, which are intended to be worn at different temperatures. Both those higher and those very low.
The purpose of this layer is damping the pressure on the Surface, protection against abrasion, in the case of models which do not contain fiber Coolmax its composition also thermal insulation. The models that are worn in the summer terry layer is combined with a special, breathable and anti-bacterial composition (Coolmax, Natural Cotton, Amicor or Prolen Siltex).
All of these models are suitable for long-term wear for people who work in extreme field conditions (eg. building), or intensely active in sports - terry layer protects the foot and composition guarantees breathable and antibacterial qualities.
2 Comfort System
non-compression double welt provides high comfort.
3 Air Control System
a system of ventilation ducts helps to maintain optimal air exchange draining the moisture and excess of heat outside.
4 Absorber system
triple weave of „3D” fibers absorbs foot pressure on the surface.
5 Anatomy System
heel „Y” type, respectively shaped knit perfectly fits to the foot and stabilizes the foot in the shoe.
6 Rosso System
flat seam at the toes prevents chafing and provides comfort of use.
7 Stick System
additional welt on the midfoot stabilizing the sock on the foot.
The selection of suitable socks can greatly increase comfort at work and in everyday life. Advanced technologies used in the manufacture of materials and socks make the feet are less tired and better cared for.
Fabrics used in socks:
Coolmax
technical fiber to ensure moisture away from the body, provides long-term air circulation and dryness, protects the foot from chafing.
Prolen Siltex
yarn modified with an antibacterial agent based on biogenic ions of silver (Ag +), inhibits the growth of bacteria, fungi and mold, reduces odor, maintains biological balance of the skin, provides a long-lasting feeling of freshness, is safe for the user and the environment.
Amicor
technical fiber responsible for antibacterial and antifungal properties, it contains a formulation to prevent the growth of bacteria responsible for odor of sweat and a mix of preparations disposing of microorganisms that serve as food for mites.
Natural cotton
natural cotton guarantees wearing comfort, high strength, excellent thermal insulation, dryness, skin breathing alloys and hypoallergenic qualities.
Merino wool
natural merino wool ensures excellent thermal insulation, long-lasting feeling of dryness and provides respiration of the skin.
Kevlar
fiber with technical properties, has a very high tensile strength and thermal performance, guarantees the size stability and high resistance to wear.
Thermolite
modern fiber for thermal qualities, provides the ideal thermal comfort at extremely low temperatures, while helping in draining moisture outside the sock.