Depending on the type of eye and face protection equipment there is the following division of products:
Products with a specified welding filter
| Produkt | The degree of aperture |
|---|---|
 gog-circle gog-circle | 5 |
 gog-cirsma gog-cirsma | 5 |
 gog-rectangle gog-rectangle | 5 |
 otw otw | 11 |
 otw-hand otw-hand | 11 |
 univer-otw univer-otw | 11 |
 otw-autoshield otw-autoshield | 9-13 |
 otw-hand-dr otw-hand-dr | 10-11 |
 otw-hand-tw otw-hand-tw | 10-11 |
- Safety glasses. There are glasses with or without side shields. The lenses are made of toughened glass or plastic. Lenses which incorporate protective filters, depending on the type of filter applied, may protect against UV radiation, infrared radiation or sharp light.
- Clear lenses without any protective filters protect against chips of solid substances or liquid splashes.
- Safety goggles. Due to their construction goggles offer a tighter fit around the eyes than glasses. Usually they feature solutions which prevent the lenses from steaming up (ventilators, anti-fog coating etc.). If a worker has contact with harmful chemicals, the goggles must feature indirect ventilation system.
- Face protectors. These protectors are made of plastic or metal mesh. Face shields made of plastics may feature filters protecting against harmful radiation.
The protectors can be adjusted to the work in various conditions depending on their structure and applied material. A special structure may protect the neck and chin. - Short shell welding helmets. They consist of a shell, frame, base and filter and provide protection of the entire face during welding. Depending on the type of filter, there are welding helmets with auto-darkening and passive filters. The short shell welding helmets can be mounted on the head by overhead adjustment band or can be attached to a protective helmet.
- Welding mask. The main difference between welding masks and welding helmets is that the former are hand held by the user. They protect the eyes, face and neck of the user.
Potential dangers caused by wavelength dangerous to the eye.
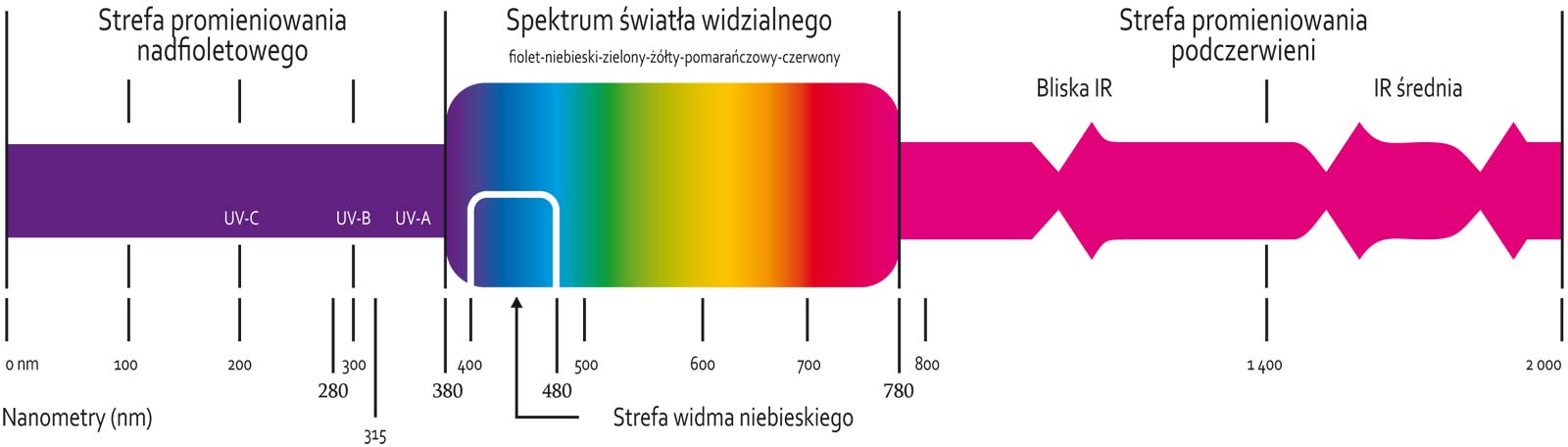
| Band | Wavelength | Environment | Hazards | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UV-C | 100-280 nm | Industrial environment, arc welding. | Corneal or lens injuries. Vision loss. | |
| UV-B | 280-315 nm | Sunlight. Industrial light. | Arc eye, welder’s flash, cataract. | |
| UV-A | 315-380 nm | Work in the open air. | Eye fatigue. Cornea: conjunctivitis, partial blindness. Pupil: cataract, premature aging | |
| Blue light | 400-480 nm | Industrial environment. Working with CRT monitors (working with a computer - tired eyes), electrical installations. Work in the open air. | Retinal injury. Vision loss. Macular degeneration (aging). Retinitis pigmentosa. | |
| Visible light | 380-780 nm | Any environment. | Retinal injuries - vision problems | |
| Infrared | 780-1400 nm (near IR) 1400-2000 nm (medium IR) | Electrical welding. Glass and steel casting. Microwave processes, sunlight. | Retinal injury. Macular degeneration (aging). Retinitis pigmentosa (near IR). Corneal or lens injuries (medium IR). |
Tasks and the characteristics of eye and face protection products
The principal task of eye and face protection equipment is the protection against:
- Mechanical risks,
- Chemical and biological risks,
- Thermal risks,
- Harmful light radiation (in visible and invisible spectrum).
The most frequently used eye protectors are safety glasses with side shields, goggles and face protectors (full face and made of mesh).
For the protection against chemicals and biological risks adequate goggles and face shields are used. The use of safety glasses for this purpose is not allowed. The aim of such protectors is to prevent the direct contact of the skin and eyes with hazardous substances.
Protection against optical and thermal radiation is provided by safety glasses, goggles and masks which feature various filters depending on the type of protector. For the protection during welding, goggles and welding protectors are used.
Protection of the eyes against direct sunlight, which is the most common risk factor for those who work in the open air or drive vehicles, is provided by glasses with adequate filters, including such which protect against UV radiation. Some types of filters may improve the contrast.
Anti-FOG

Anti-fog coating (Anti-fogging) feature chemical substances which prevent the condensation of vapour in the form of small drops on the surface of the lenses. It is manufactured during complex production processes by adding Anti-Fog chemicals to the plastics at the time of their production. Applied also in the form of a surface film or hydrophilic coating on the surface. It is also available in spray, cream and gel or as an ingredient of moisturized tissues.
Anti-fog coating is used in glass lenses and plastics applied in optical products such as lenses, glasses, goggles or photographic and binoculars objectives.
Selection of the degree of dimming depending on the technology and welding current
| Welding process | Welding current (A) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5 | 6 | 10 | 15 | 30 | 40 | 60 | 70 | 100 | 125 | 150 | 175 | 200 | 225 | 250 | 300 | 350 | 400 | 450 | 500 | 600 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| MMAW (covered electrode) | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MAG | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TIG | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MIG | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MIG with light alloys | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Air carbon arc gouging | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Plasma cutting | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Plasma arc welding | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
List of standards for eye and face protection equipment
Industrial hazards
| Mechanical risks | dust, impact, solid particles |
| Thermal risks | hot liquids, molton metal splashes, flames |
| Chemical and biological risks | splashes of acids, solvents, bases, infected blood |
| Radiation | ultraviolet, infrared, visible light, laser |
| Electricity | direct contact with electricity, short circuit electric arc |
Facts about eye injuries
Every day more than 600 persons all over the world suffer from eye injuries only because they chose not to use protective eyewear
EN166
Personal eye protection. Requirements.
The standard is applied to all personal eye protection equipment used to provide protection against risks which occur in industries, laboratories etc. The standard is not applicable if more specific standards exist, unless such standards refer to this standard. Eye protection equipment featuring corrective lenses is not excluded from the thematic scope of this standard.
The standard defines a wide range of requirements for application of filters and frames.
Parameters of filters/lenses
The marking of the filter must contain:
- Code number of the filter and the marking of protection level and obscuration level (for filtering lenses),
- Manufacturer’s symbol,
- Marking of optical class,
- Mechanical resistance symbols,
- Application symbols.
- Optical class - has to be specified. There are 3 classes:
- CLASS 1 - suitable for continuous use. Refractive power of +0.06 diopters,
- CLASS 2 - suitable for intermittent use. Refractive power of +0.12 diopters,
- CLASS 3 - suitable for occasional use, must not be worn continuously. Refractive power of +0.12/-0.25 diopters.
- Mechanical strength of lenses:
- Lack of marking - minimum impact resistance,
- S - increased robustness (resistance to the impact of a steel ball with a nominal diameter of 22mm and minimum weight of 43g travelling at 5,1m/s),
- F - Lenergy impact (resistance to the impact of a steel ball with a nominal diameter of 6mm and minimum weight of 0.86g travelling at 45m/s),
- B - Medienergy impact (resistance to the impact of a steel ball with a nominal diameter of 6mm and minimum weight of 0.86g travelling at 120m/s),
- A - Hienergy impact (resistance to the impact of a steel ball with a nominal diameter of 6mm and minimum weight of 0.86g travelling at 190m/s),
- K - surface resistance to scratches made by small particles,
- N - fog resistance,
- 8 - resistance to short circuit electric arc,
- 9 - resistance to molten metal and hot solids
- T - tests conducted in extreme temperatures <-5°C, +55°C> (optional). ATTENTION: A is applicable only to face protectors, B may apply to goggles and face protectors, F may apply to any eye protection equipment.
Parameters of frames
The marking of the frame must contain:
- CE symbol,
- Manufacturer’s identification mark,
- Number of the EN166 standard (obligatory),
- Symbols of fields of use and results of mechanical strength tests.
- Mechanical strength of frames:
- Lack of marking - minimum strength. The field of use is not defined,
- S - increased robustness (resistance to the impact of a steel ball with a nominal diameter of 22mm and minimum weight of 43g travelling at 5,1m/s),
- F - Lenergy impact (resistance to the impact of a steel ball with a nominal diameter of 6mm and minimum weight of 0.86g travelling at 45m/s),
- B - Medienergy impact (resistance to the impact of a steel ball with a nominal diameter of 6mm and minimum weight of 0.86g travelling at 120m/s),
- A - Hienergy impact (resistance to the impact of a steel ball with a nominal diameter of 6mm and minimum weight of 0.86g travelling at 190m/s).
- Fields of use of frames:
- Lack of marking - for general use, no specified mechanical risks or risks caused by excessive UV radiation, infrared radiation, sunlight or visible radiation,
- 3 - liquids – droplets and splashes,
- 4 - large dust particles. Dust particle size of above 5 micrometers,
- 5 - gas and fine dust particles – gases, fogs, aerosols, smoke and dust with particles smaller than 5 micrometers,
- 8 - shocircuit electric arc,
- 9 - hot metals and molten solids.
Types of lenses
| Code | Name | Description | LTV |
|---|---|---|---|
| ut | Clear Uncoated | The lenses provide basic protection against splinters. | 85% |
| t | Clear | They provide excellent optical properties for general applications, where it is necessary to protect sight against splinters. | 85% |
| s | Gray | The lenses ideal for work in the open, where risk of blinding occurs. | 12% |
| ms | Gray Mirror | The lenses ideal for work in the open, where risk of blinding occurs. They have a reflective layer. | 12% |
| em | Emerald | Applicable outdoors, as a protection against sun blinding. | 9% |
| mem | Emerald Mirror | Applicable outdoors, as a protection against sun blinding. | 9% |
| y | Amber | Amber-yellow color block blue part of the light spectrum to ensure maximum contrast., Especially in low light conditions. | 85% |
| 30-z | Light green, filtr 3.0 | General purpose glass to protect against glare. Aperture 3 according to DIN. | filtr 3.0 |
| 50-z | Dark green, filter 5.0 | General purpose glass to protect against glare. Aperture 5 according to DIN. | filtr 5.0 |
| br | Brown | The lenses ideal for work in the open, where risk of blinding occurs. Ideal for drivers - they do not reduce recognition of colours applied in road signalisation. | 12% |
| mt | Clear Mirror | The lenses provide higher light permeability for application indoors and in open spaces. The lenses reduce blinding from artificial sources of light, such as halogen lights and others. | 55% |
| jn | Light blue | The lenses provide higher light permeability. For application indoors and outdoors. The lenses reduce blinding from artificial sources of light, such as halogen lights and others. | 70% |
| n | Blue ice | They protect against direct blinding. | 33% |
| mn | Blue Mirror | Blue mirror lenses. They protect against direct blinding. They reduce blinding from artificial sources of light. | 33% |
| mnd | Blue Diamond | Blue-diamond mirror lenses. They protect against direct blinding. They reduce blinding from artificial sources of light. | 33% |
EN169
Personal eye protection. Filters for welding and related techniques. Transmittance requirements and recommended use.
The standard specifies marking and requirements for transmittance rate of filters designed for eye protection equipment for welders, users of braze welding devices, electric arc and plasma torches.
If protectors with auto-darkening filters are used, the provisions of EN379 standard shall apply.
EN170
Personal eye protection. Ultraviolet filters. Transmittance requirements and recommended use.
The standard describes mode of marking and identification and requirements for transmittance rate of filters protecting against UV radiation. The standard also contains guidelines for selection and use.
EN172
Personal eye protection. Sun glare filters for industrial use.
The standard specifies marking, transmittance rates and appropriate test methods for sun glare filters. Other requirements for this type of filters are listed in the EN166 standard.
EN1731
Personal eye protection - Mesh eye and face protectors.
The standard specifies the materials, design, requirements, test methods and marking of mesh eye and face protectors which protect against mechanical risks.
The standard does not refer to eye and face protectors against liquid splashes (containing molten metal particles), hot particles, electrical risks, UV and infrared radiation. It does not apply to mesh eye and face protectors used by hockey players, fencers or in paintball.
EN175
Personal protection. Equipment for eye and face protection during welding and allied processes.
The standard specifies safety requirements and test methods for personal eye and face protection equipment against harmful optical radiation and other specific sources of risk and danger which usually occur during welding, cutting or allied processes.
EN14594 (supersedes EN1835)
Respiratory protective devices. Continuous flow compressed air line breathing apparatus with a helmet or hood. Requirements, testing, marking.
The standard specifies minimum requirements for continuous flow compressed air line breathing apparatus with a helmet or hood which is designed for use in gas and/or dust polluted atmospheres. Such apparatus is used, apart from escape respirators, diving regulators and apparatus used in abrasive blasting, at work positions where the risk of damage to hose supplying compressed air is low and the user’s moves are limited. It describes laboratory tests which enable the assessment of conformity with the requirements.
EN379
Personal eye protection. Auto-darkening welding filters.
The standard concerns welding filters which automatically adjust transmittance rate depending on the presence of a welding arc (referred to as auto-darkening welding filters).
EN61000-6-2
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) - Part 6-2: General standards. Resistance in industrial environments.
The standard specifies requirements concerning various phenomena of continuous or intermittent nature, occurring as a result of conduction or radiation, electrostatic discharge associated with electronic and electrical devices designed for industrial use, with respect to which there are no standards concerning a specific article or a group of articles.
EN61000-6-3
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) - Part 6-3: General standards. Emission standard for residential, commercial and light-industrial environments.
The standard specifies emission requirements for all electronic and electrical devices intended for use in residential, commercial and light-industrial environments not covered by detailed standards.