Protective clothing belongs to the category of commonly used personal protective equipment which protect worker’s body against basic risks at the workplace.
According to 89/686/EEC directive on safety requirements and protection of workers’ health by using personal protective equipment at workplace products are divided into three safety categories depending on the risk level to which a worker is exposed while performing a given type of work.
Categories of protection
When it comes to body protection the division looks as follows:
CATEGORY I
Protective clothing against minimum risks.
This category of protective clothing includes garments with a simple structure whose protective properties are evaluated by the user.
If the risk increases, the results may be easily identified at the right time by the user.
Category I includes in particular garments which protect against:
- harmless impurities (mild cleaning agents etc.) whose effects are easily reversible,
- mechanical damage to the surface,
- risks connected with heat assuming that the risk is low,
- weather conditions (low temperature, rain).
CATEGORY II
Protective clothing which does not protect against minimum risks (cat.I) and life threatening and health threatening risks (cat.III).
Category II includes garments which protect against a specific danger which is not life or health threatening and does not cause a permanent health impairment.
Examples of clothing which belongs to category II:
- Garments which protect against cuts,
- Garments which reduce the dangers which occur during welding - for welders and similar professions,
- Warning clothing (for road maintenance workers).
CATEGORY III
Protective clothing with a complex structure protecting workers against life and health threatening situations.
Category III includes specialist protective clothing whose aim is the protection against factors which could be very dangerous to the worker and whose direct effects cannot be identified at the right time.
This group includes among others:
- Specialist chemical protective suits,
- Clothing which protects against ionizing radiation, flames, temperature above 100°C or large splashes of hot substances,
- Clothing which protects against low temperatures (below - 50°C),
- Clothing intended for works with high voltage.
Protective qualities of these garments are determined first and foremost by the features of fabrics used (thickness, impregnation, special weave type) and production techniques applied (special seams).
With regard to the body parts which are protected, protective garments may be divided into:
- Torso protective clothing,
- Protective clothing for parts of the torso,
- Head protective gears.
Clothing care and maintenance symbols
|
|
Chemical protective clothing types
summary of standards which specify the requirements for clothing of each category::
| Standard | Type | Ensured chemical protection |
| EN13034 | 6 | against splashes |
| EN13982-1 | 5 | anti-dust (asbestos) |
| EN14605 | 4 | against fumes |
| EN14605 | 3 | against liquid chemicals |
| EN943-1 | 2 | lack of gas-tightness |
| EN943-1 EN 943-2 | 1 | gas-tight chemical protective suit |
There are six types of garments which protect against chemicals (1-6) where the first type provides the lowest degree of protection and the sixth type provides the highest degree of protection:
- Type 1 - protection against chemicals, it ensures gas-tightness:
 Type 1a - with air supplied from sources other than air from the atmosphere by appropriate apparatus installed inside the chemical protective suit.
Type 1a - with air supplied from sources other than air from the atmosphere by appropriate apparatus installed inside the chemical protective suit.- Type 1b - with air supplied from sources other than air from the atmosphere by appropriate apparatus installed outside the chemical protective suit.
- Type 2 - protection against chemicals, it does not ensure gas-tightness.
 Type 3 – protection of the whole body, it features connections which prevent liquid penetration between various elements of garments.
Type 3 – protection of the whole body, it features connections which prevent liquid penetration between various elements of garments. Type 4 – protection against fumes of liquids. It features solutions which ensure tightness between various elements of garments.
Type 4 – protection against fumes of liquids. It features solutions which ensure tightness between various elements of garments. Type 5 - it provides protection against airborne solid particles.
Type 5 - it provides protection against airborne solid particles. Type 6 - short-term protective clothing protecting against light sprays and splashes.
Type 6 - short-term protective clothing protecting against light sprays and splashes.
List of standards applicable to body protection
EN ISO 13688 (supersedes EN340)

Protective clothing. General requirements.
This international standard specifies general requirements concerning performance, innocuousness, ergonomics, size designation, ageing, compatibility and marking of protective clothing and information to be supplied by the producer with the protective garment.
This international standard is intended to be applied in combination with other standards specifying the requirements for specific protective performance and cannot be used on a stand-alone basis.
EN510

Requirements for anti-entanglement with moving parts protective clothing.
The standard specifies basic requirements for clothing used when there is a risk of entanglement with and being pulled into moving parts of machines.
The requirements set forth in the standard describe the structure of clothing, buckling elements and fabrics designed to be used in this type of garments. The standard mentions test methods presented in EN340.
According to the standard, the clothing should adhere to the body and be devoid of any elements which could entangle with moving parts of machines.
EN342

Protective clothing. Clothing sets and articles protecting against cold.
This standard describes the properties of protective clothing against cold in temperatures below -5°C. There are two types of protective products: clothing articles and clothing sets.
EN14058

Protective clothing. Clothing articles protecting against cold.
This standard specifies requirements and detailed test methods for clothing articles such as: vests, jackets, trousers protecting against cold climate conditions.
These garments are supposed to provide protection in moderately low temperatures (-5°C and above) to protect the skin and body against localized skin and body cooling. They can be used both inside buildings and in the open air.
The clothing is not required to be made of waterproof and airtight materials - it is optional.
EN343

Protective clothing. Protection against rain.
This standard specifies the properties of protective clothing against bad weather conditions, wind and low temperature of above -5°C.
| A | Water proofness (from 1 to 3). It refers to the amount of water coming through the clothing materials, |
| B | Water vapour permeability (from 1 to 3). It refers to the breathability of the clothing. |
ATTENTION: If there is an X instead of a number value, it means that the product has not been subject to any tests in the area in question.
EN ISO 20471 (supersedes EN471)

High visibility clothing for professional use. Test methods and requirements.
This international standard specifies the requirements for high visibility clothing which visually signals the user’s presence to the operators of vehicles and other mechanical devices regardless of the lighting, in the daylight and at night when illuminated by vehicle lamps. It contains requirements for colour and reflectivity of the garments as well as for the minimum surface and distribution of materials.
EN1150
Protective clothing. Visibility clothing for non-professional use. Test methods and requirements.
Utility specified optical requirements for garments of high-performance visibility to be worn by adults and young people in non-professional conditions. This type of clothing is intended to signal the user’s presence visually on urban roads. The standard does not include accessories worn by people or attached to clothing.
EN1073-2

Protective clothing against radioactive contamination. Requirements and test methods for non-ventilated protective clothing against particulate radioactive contamination.
EN1149-1

Protective clothing. Electrostatic properties. Test method for measurement of surface resistivity.
This standard specifies minimum electrostatic requirements and test method for electrostatic dissipative clothing with the aim of preventing the appearance of sparks which could cause fire. These requirements are not sufficient when working in flammable environments with increased oxygen levels and the test method is not appropriate for fabrics which contain fibers with conductive core. This standard does not apply to mains voltage.
EN1149-3

Protective clothing. Electrostatic properties. Test methods for measurement of charge decay.
This standard describes test methods for measurement of static charge decay from the surface of clothing material. The test methods presented in the standard apply to all materials, including homogenous and non-homogenous materials, which contain fibers capable of surface conductivity and fibers with conductive core.
EN1149-5

Protective clothing. Electrostatic properties. Material performance and design requirements.
The requirements concern marking of the garments and the content of manufacturer’s instruction manual. According to these requirements, a fabric is classified as electrostatic dissipative if:
- t50 < 4 s or S > 0.2, where: t-50 - half decay time on material charged by induction, S - shielding factor, S = 1 - ER/Emax (Emax - electric field strength with no test specimen present, ER - electric field strength on the other side of the test specimen);
- surface resistivity is lower or equal to 2.5 x 109 Ω at least on one side of the tested material.
If the material contains conductive yarn in parallel threads or in the form of a network, the distance between conductive threads in one direction should not exceed 10mm in each clothing element.
This document also determines the requirements for structure of clothing. When used, electrostatic dissipative clothing should cover entire body, also when the user is performing standard operations or bending down. At the same time it cannot limit the moves of the user when it is buttoned up in accordance with the recommendations of the producer. If the clothing is made of combination of materials, the anti-static material should constitute the external surface. Any zippers, buttons or snap fasteners made of conductive materials have to be covered with anti-static material.
The manufacturer of electrostatic dissipative clothing is obliged to attach to each product an instruction manual which contains the following information:
- the worker is not allowed to take off the anti-static clothing in explosive atmosphere or in close proximity of flammable materials,
- instructions as to the manner of handling the clothing,
- anti-static properties of the clothing may change (as a result of the presence of impurities, damage or washing),
- the user of anti-static clothing should be properly grounded by leakage resistance lower than 108 Ω,
- electrostatic dissipative clothing cannot be used in atmosphere with increased oxygen levels without the prior consultation with OSH worker (specialist).
In an explosive atmosphere, oxygen enriched atmospheres or in the proximity of flammable materials the worker should be directly grounded or grounded by adequate footwear (leakage resistance should be lower than 105 Ω) in accordance with PN EN ISO 20345:2007.
In conformity with the requirements of the standard dielectric elements of clothing articles such as a company logo, labels, reflective straps cannot be used unless they are permanently fixed to the surface of anti-static material.
EN469

Protective clothing for firefighters. Requirements and test methods for protective clothing for firefighting.
This standard defines test methods and minimum requirements for clothing used in firefighting and related operations when there is a risk of damage as a result of heat and/or flames. The standard specifies the general construction of garments, minimum degree of performance of applied materials and methods of determination of such degree.
EN11611 (supersedes EN470-1)

Protective clothing for use in welding and allied processes.
This standard defines basic minimum requirements and test methods for protective clothing dedicated to welders and workers who perform similar work of comparable risk level.
This type of clothing aims to protect the user against:
- Molten metal splashes,
- Burning as a result of short-term contact with flames,
- Heat radiation,
- UV radiation produced by electric arcs.
EN470-1 (superseded by EN11611)

Protective clothing for use in welding and allied processes. Requirements.
This standard describes test methods and requirements for protective clothing used by welders and workers who perform similar operations of comparable risk level.
This type of clothing is used as a protection against small molten metal splashes, short-term contact with flames and UV radiation and is worn for 8 hours without breaks in the conditions resulting from a given profession.
EN11612 (supersedes EN531)
Protective clothing - Protective clothing against heat and flame.
The standard defines requirements for clothing made of elastic fabrics which aims to protect user’s body, excluding the hands, against heat and/or flame.
With respect to head and feet protection the standard concerns only leggings, shoe protectors and hoods, excluding eye protection solutions and respiratory protective equipment if they are included in the hood.
The standard covers a wide range of protective clothing which should be flame retardant and demonstrate resistance to at least one of the following agents:
- Thermal radiation,
- Heat permeation when in contact with a hot object,
- Convective heat permeation,
- Molten metal splashes.
The standard does not apply to protective clothing for firefighters and welders.
EN531 (superseded by EN11612)
Protective clothing for workers exposed to heat.
This standard applies to protective clothing for workers exposed to heat.
These garments include external elements made of a flexible material which protects particular body parts. Hoods and leggings are also included, unlike protective articles for: head, hands and feet.
The standard specifies requirements and test methods for materials to be used in the production of protective clothing and provides recommendations for the design of garments.
The clothing covered by this standard is intended for industrial workers to protect them against short-term contact with fire (A code) and at least one type of heat.
Heat types:
| Code | Heat type |
| B | Convective heat |
| C | Thermal radiation |
| D | Large molten aluminum splashes |
| E | Large molten iron splashes |
Retroreflective materials are treated as accessories. To be approved for use in this type of clothing they have to be certified according to EN532 standard.
EN15025 (supersedes EN532)
Protective clothing - Protection against heat and flame. Test method for limited flame spread.
This standard defines the performance requirements for limited flame spread with respect to materials, sets of materials and protective clothing with the aim of reducing the probability of ignition of clothing which would make it dangerous, as well as additional requirements for garments.
Protective clothing included in this standard is designed to protect workers against accidental and short-term contact with small flames when there is no serious danger from heat and no other forms of heat are present.
If there is a need for extra protection against heat beside the protection against limited flame spread, ISO 11612 standard will be more appropriate.
EN532 (superseded by EN15025)
Protective clothing. Protection against heat and flame. Test methods for flame spread.
This standard specifies methods of testing the reaction of materials to fire and flame spread.
EN14116 (supersedes EN533)
Protective clothing - Protection against heat and flame. Materials, sets of materials and limited flame spread clothing.
This standard describes the test method for limited flame spread on materials intended for clothing protecting against heat and flame, conditions of testing the materials in case of small flame acting on vertically positioned textile samples and samples of industrial articles which are composed of one or more elements (coated, quilted, multilayer, sandwich and similar combinations).
EN533 (superseded by EN14116)
Protective clothing - Protection against heat and flame. Limited flame spread materials and arrangement of materials.
The standard defines minimum requirements for limited flame spread properties of materials and their arrangements used in protective clothing.
The classification system refers to materials and arrangements tested in accordance with EN 532 before and after a standard cleaning procedure.
EN13034 (TYPE 6)

Clothing protecting against liquid chemicals. Requirements for clothing which provide limited protection against liquid chemicals (Type 6 and Type PB[6] clothing).
The standard specifies minimum requirements for limited use and reusable protective suits against chemicals (type 6). This standard also defines minimum requirements for connections between various parts of clothing by conducting a test which verifies the influence of sprays on a suit, which is a variety of EN468:1994 standard.

Two basic tests mentioned in EN13034 standard are taken from EN368 (textiles) and EN468 (clothing) standards. EN368 alone is not enough to approve this type of clothing for use.
Such clothing provides limited protection against liquid aerosols, sprayed liquids and minor sprays where the potential risk type, such as sprayed liquids and fogs, is specified.
EN13982-1 (TYPE 5)

Protective clothing for use against solid particles. Requirements for chemical protective clothing providing protection to the entire body against airborne solid particles (type 5 clothing).
This standard specifies minimum requirements for chemical protective clothing impenetrable to particles (type 5) and resistant to permeation of solid particles.  This type of clothing is made of impenetrable materials and features airtight connections which prevent particle penetration and connections between various elements such as flying caps, gloves, shoes, glasses, facemasks which can be listed in other EU standards. These clothing articles may rank among clothing providing protection to the entire body, such as connections between one or two components, with or without a flying cap or glasses, with or without integrated shoes. Required parameters: testing resistance to abrasion, resistance to cracks which result from bending, resistance to trapezoid tear, puncture and ignition.
This type of clothing is made of impenetrable materials and features airtight connections which prevent particle penetration and connections between various elements such as flying caps, gloves, shoes, glasses, facemasks which can be listed in other EU standards. These clothing articles may rank among clothing providing protection to the entire body, such as connections between one or two components, with or without a flying cap or glasses, with or without integrated shoes. Required parameters: testing resistance to abrasion, resistance to cracks which result from bending, resistance to trapezoid tear, puncture and ignition.
EN14126

Protective clothing. Requirements and test methods for protective clothing against infectious agents.
The standard states that clothing protecting against biological agents should act as a barrier to protect the entire body or some part of it against direct contact with infectious agents.
EN14325
Chemical protective clothing - Test methods and classification of materials, seams, permanent and separable connections used in clothing providing protection against chemicals.
EN14605 (TYPE 4, TYPE 3) (supersedes EN465, EN466)

Protective clothing against liquid chemicals. Requirements for clothing providing protection to the entire body, featuring liquid-tight connections (type 3) and spray-tight connections (type 4), including articles which protect only some parts of the body (types PB[3] and PB[4]).
EN943-1

Protective clothing against liquid and gaseous chemicals, including aerosols and solid particles. Requirements for ventilated and non-ventilated gas-tight (type 1) and non-gas-tight (type 2) protective suits.
EN943-2

Protective clothing against liquid and gaseous chemicals, including aerosols and solid particles. Requirements for gas-tight protective suits (type 1) intended for emergency teams (ET).
PN-83/P-22401
Saddler’s articles - terminology.
EN381-11

Protective clothing for users of hand-held chainsaws. Requirements for upper body protectors.
The standard concerns personal protection equipment intended for the protection against risks which occur during use of handheld chainsaws.
ATTENTION: None of the protective measures provides 100% protection against cuts by hand-held chainsaws. However, some degree of protection can be provided by protective equipment.
| A | Protection classes against cuts at a chain speed (0-3). | ||||||||||||||||||
| Protection class | Chain speed |
|---|---|
| 0 | 16m/s |
| 1 | 20m/s |
| 2 | 24m/s |
| 3 | 28m/s |
EN13998
Protective clothing - aprons, trousers and vests providing protection against cuts and stabs by hand knives.
The standard describes aprons, trousers and vests and other types of clothing protecting specific parts of the body against accidents involving hand knives.
The standard specifies requirements for design, puncture and cut resistance, size, ergonomic properties, water permeability, cleaning and disinfection procedures, marking and information with which the users of protective clothing are provided by the manufacturer.
The standard provides the classification of protection levels and appropriate test methods.
IEC61482-2
Live work - Protective clothing against thermal effects of an electric arc - Part 2: IEC61482-2 requirements are applied if there is a risk of contact with electric arc.
The standard specifies the requirements and test methods for materials and clothing articles used in protective clothing for electricians which protects against heat and for workers who are exposed to the thermal effects of an electric arc based on:
general properties of fabrics tested according to selected methods appropriate for such fabrics and thermal resistance to electric arc effects such as:
- resistance of materials (ATPV or EBT50) to the effects of the arc during open arc test in laboratory conditions according to IEC61482-1-1 or
- protection class of materials and clothing articles against electric arc (class 1 or class 2) during tests for resistance to direct and enforced contact with electric arc in conditions specified in IEC-61482-1-2.
This standard does not apply to the risk of electric shock. It should be applied in combination with other standards which concern such a risk.
IEC61482-1-1
Live work - Protective clothing against thermal effects of an electric arc - Part 1-1: Test methods - Method 1 - Determination of the parameters of an arc ((ATPV and EBT50) for fire retardant materials.
This standard specifies methods of determining the ATPV of materials designed to be used in the production of heat and fire resistant clothing for linemen at risk of electric arc and methods of verifying the functionality of clothing made of such materials. Method of measuring carbonization time and definitions are also provided in this standard.
IEC61482-1-2
Live work - Protective clothing against thermal effects of an electric arc - Part 1-2: Test methods - Method 2: Determination of protection class of materials and clothing against electric arc effects with the use of constrained and directed arc (box test).
This standard describes the method of testing garments and materials designed to be used in the production of heat and fire resistant clothing for linemen at risk of electric arc. The standard contains a description of test method which involves the use of constrained and directed electric arc in low voltage network to classify materials and clothing into an appropriate protection class against arc effects, and definitions.
EN ISO 22000 (HACCP)
Food safety management systems - Requirements for all organizations in the food chain.
This standard contains requirements for food safety management systems dedicated to organizations in the entire food chain, where the organization must demonstrate its ability to control food safety risks to ensure that the food products provided are safe.
The standard defines requirements which enable planning, design, implementation, maintaining and updating food safety management systems aimed at delivering a final product which complies with its intended purpose and is safe for the consumers.
The guidelines provided in the standard cover and integrate into the European standards the requirements of HACCP system (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point).
About HACCP approach
Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point is a method of quality management in the food industry which enables:
- identification and analysis of risks at various stages of food production processes
- determination of measures necessary to prevent such risks
- ensuring that such measures are implemented in an efficient manner.
HACCP method is a systematic and rational approach to food safety from microbiological, physical and chemical hazards in the food sector.
EN 12947-2
Textiles- Determination of the abrasion resistance of fabrics by the Martindale method
Part 2: Determination of specimen breakdown
This document specifies the procedure for the determination of specimen breakdown (end-point of test) by inspection at fixed intervals and is applicable to all textile fabrics including nonwovens apart from fabrics where the specifier indicates the end performance as having a low abrasion wear life.
This document is not applicable to coated fabrics (including laminated fabrics). If the abrasion behaviour of the coated surface of a coated fabric (including laminated fabrics). If the abrasion behaviouur of the coated surface of a coated fabric is to be determined, use the methods described in the various parts of ISO 5470
EN ISO 5470-2:2003
Flat textile products coated with rubber or plastics - Determination of abrasion resistance
Part 2: Martindale abrasive equipment
WARNING - It is recommended that persons using this part of ISO 54070 are familiar with the normal laboratory procedure. This part of ISO 5470 is not intended to draw attention to all matters concerning health and safety and ensures compliance with national regulations.
This Part of ISO 5470 provides two separate methods for determining the wet and dry abrasion resistance of materials. They apply to the coated surface or flat surfaces of coated textile products. If the abrasion resistance of the uncoated surface of the product has to be determined, use the methods for uncoated textiles described in various parts of ISO 12947.

Leber & Hollman
Durability - High Technology Fabric

High Technology Fabric (HTF) is a production technology which provides the material with exceptional durability and ensures that the products manufactured with the use of this technology are very comfortable.
HTF
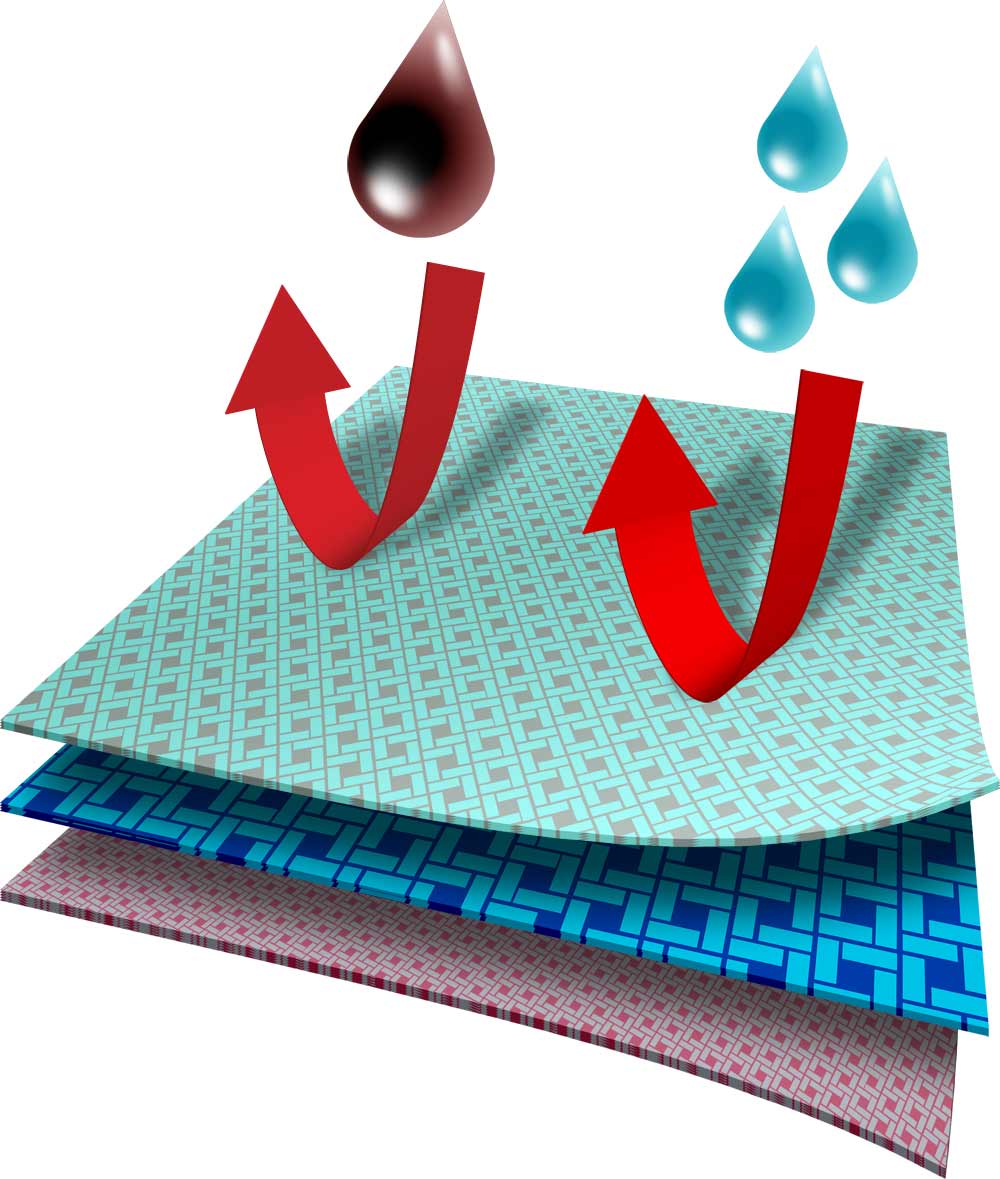
Depending on the type of finish, the outer surface is made of polyester - it is very durable, resistant to grease and oils and prevents easy water penetration, or 100% cotton.
The inner surface is made of cotton to ensure a high degree of comfort.
HTF refers not only to the fabric but also to the method of its preparation for production and chemical finishing at the final stage of the production process. HTF uses a unique method of weaving for clothes with external surface made of cotton to increase the durability of the fabric by applying a special finish on the outer surface.
Types of finish
Depending on the application of clothing we offer the following finish types:
 | HTF+ | a finish which provides enhanced resistance to water and oils thanks to a special coating. |
 | HTFC | made of 100% cotton |
 | HTF | outer surface made of polyester, inner surface made of cotton which ensures high degree of comfort. |
 | HTFXP | provides protection against rain and wind but maintains breathability. Secured seams. |
Search for products with HTF logo!
Comfort - Easy Fit System


Easy-Fit System (EFS) ensures freedom of moves and snug fit in every situation.
Elastic insert hidden under the belt provides you with extreme comfort and adjusts the fabric to your moves.
Whether you stand on your feet, walk, sit or crouch, your moves will not be limited and you will always feel comfortable.
EasyFit system is a guarantee of your comfort!
Quality - Quality Comfort Technology
The priorities of the Quality Comfort Technology are the comfort of its users and superior quality of products.
These goals are possible to reach thanks to a careful design of each new product and numerous tests conducted prior to the introduction of the product on the market. The aim of these tests is to verify that our Customers will be satisfied with the range of products offered by Leber & Hollman.
QCT also means a continuous quality monitoring at the assembly lines - our experienced team of experts verify each product manually. This means that our Customers will receive a product of a superior quality which will meet their expectations.
QCT involves continuous improvement of applied processes to make future products even better.
Leber & Hollman - quality and comfort without compromise!

OEKO-TEX®
OEKO-TEX® Standard 100 is a world-leading testing and certification system for textiles. According to OEKO-TEX® Standard 100 products are free from harmful substances in concentration which may affect human health, e.g. pesticides, chlorophenols, formaldehyde, colorants which can induce allergies, prohibited azo colorants and extractable heavy metals.
To comply with OEKO-TEX® Standard 100 standards all the components of a product, i.e. the external material, threads, lining, prints and accessories such as buttons, zippers, rivets etc, have to satisfy the required criteria.

About SOFTSHELL®
Advanced technology of production of high-quality clothing which consists in the connection of two or three layers of clothing together to increase the comfort and provide protection against changing weather conditions.
Softshell technology enables users to remain in changing weather conditions for a long period of time without the need to change clothes and prevents the risk of hypothermia or hyperthermia.
What is characteristic of clothing manufactured with the use of Softshell technology is its low weight.
SIOEN - types of materials

FLEXOTHANE®
Flexothane® is a technological material which provides optimum protection. Polyurethane coating on a stretchy knitted surface makes Flexothane resistant to water and wind, ensures high degree of comfort, does not emit irritating sounds. The material stretches up to 150%, is comfortable and resistant to abrasion and can be machine washed.
-
 Flexothane® Essential : around 170g/m², one sided PU coating on an undyed polyester fabric.
Flexothane® Essential : around 170g/m², one sided PU coating on an undyed polyester fabric. -
 Flexothane® Classic : around 180g/m², one sided PU coating on a dyed polyamide fabric.
Flexothane® Classic : around 180g/m², one sided PU coating on a dyed polyamide fabric. -
 Flexothane® Flame : one sided PU coating on an undyed polyester fabric, fire retardant.
Flexothane® Flame : one sided PU coating on an undyed polyester fabric, fire retardant. -
 Flexothane® Kleen : one sided PU coating on an undyed polyamide fabric, to be washed at a maximum temperature of 95°C, antibacterial properties.
Flexothane® Kleen : one sided PU coating on an undyed polyamide fabric, to be washed at a maximum temperature of 95°C, antibacterial properties.
FLEXOTHANE® FR INDEX 1 AST (anti-static fabric)
A combination of fire retardant polyurethane on a fire retardant polyamide fabric with anti-static properties.
FLEXOTHANE® FLAME ARC
Waterproof fabric which protects against cold and wind, fire retardant, electric arc resistant.
FLEXOTHANE® ARC
Waterproof material which protects against cold and wind. It is fire retardant and provides protection against electric arc.
FLEXOTHANE® FR INDEX 3 AST
A combination of fire retardant polyurethane coating on an elastic fire retardant aramid fabric. It has anti-static properties.
Flexothane® properites:
Resistance to water and wind: welded and stitched seams. All seams are stitched and then high frequency welded. They are waterproof with a clean finish.
Breathable fabric, extremely comfortable. Flexothane® is a breathable fabric. It absorbs sweat which prevents the unpleasant feeling of the fabric clinging to the skin. The skin remains dry and the body temperature is under control.
Durable, comfortable, light, noise free. Flexothane® is resistant to difficult working conditions and bad weather. Moreover, it is very comfortable and stretches up to 150% which ensures freedom of moves. Garments made of Flexothane® are suitable for use for a very long time.
Possibility of washing in a washing machine. Flexothane® is resistant to oil derivatives, petrol, fuel oils, grease. The smooth PU surface is very easy to clean. Flexothane materials can be washed in washing machines (Kleen at a temperature of up to 95°C) without the loss of original shape. Flexothane® users do not have to worry about any stains.
Colours. Flexothane® is available in many colours.
Environment-friendly. Flexothane® is manufactured in Mouscron, Belgium, at a plant where environmental policy is actively implemented. Flexothane® clothing can be recognized by details: fasteners, heat-sealed label, Flexothane® mark on the lining, colourful tag and Flexothane® labels.
Washing instructions. Washing temperature: Flexothane 40°C, Kleen 95°C; Chlorination: do not chlorinate; ironing: do not iron; drying; cleaning: mechanical cleaning.




SIOPOR®

SIOPOR
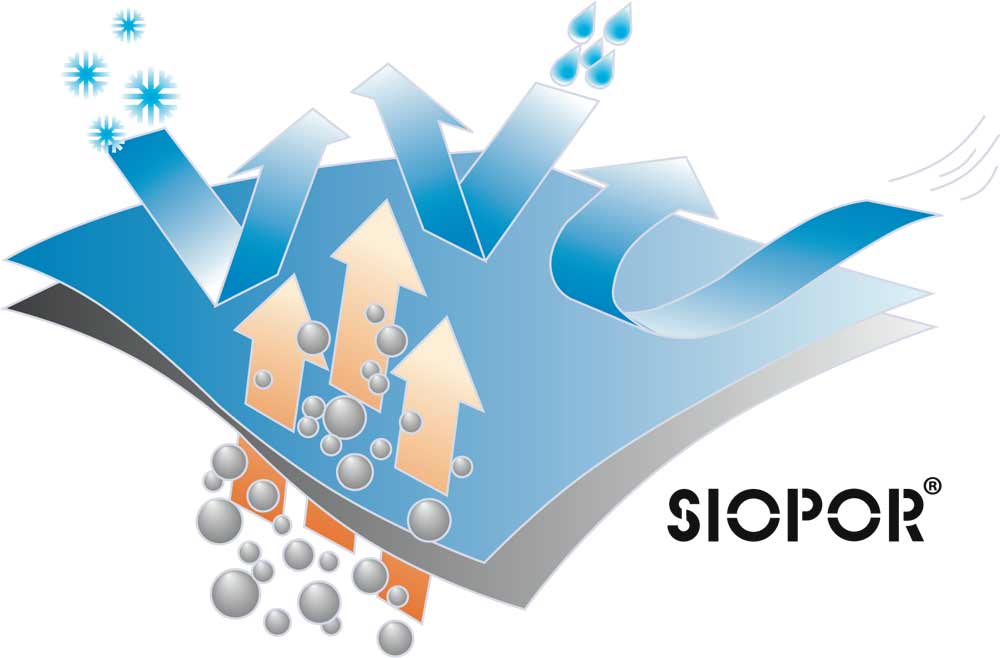
protection
Thanks to a hydrophilic PA or PES outerlayer Siopor® keeps you warm and dry. It is resistant to water and wind, breathable, comfortable and can be washed in a washing machine. High degree a breathability ensures full comfort of work in all weather conditions. Siopor® FR AST is fire retardant and anti-static.
Characteristics:
- waterproof
- wind resistant
- comfortable
- breathable
- suitable for machine washing
- lightweight
SIOPOR parameters
SIOPOR® Regular: around 160g/m², nylon or polyester external coating with a hydrophilic layer of PU on the inside.
SIOPOR® Triple: three layers of material, 100% polyester, 100% PU membrane and an internal layer of 100% polyamide.
SIOPOR® FR AST: smooth surface, anti-static, fire retardant, available also in reflective colours.
SIOPOR® Regular FR: smooth PA coating, fire retardant, available in reflective colours.
SIOPOR® Mega: twill weave PA coating, available also in reflective colours.
SIOPOR® Micro: soft polyester micro fibers, 135Gr/m2.
SIOPOR® Ultra: around 200g/m², 100% breathable PES, 100& PU coating.
SIOPOR® Extra: around 210g/m², 100% breathable PES, 100& PU coating.
SIOPOR properties
Resistant to water and wind: welded seams. The protective clothing is welded with the use of an advanced heat sealing technology which guarantees maximum water tightness. Hydrophobic finish prevents water absorption through the outer coating.
Suitable for machine washing. It has a protective layer which increases the resistance to dirt and oils thanks to which garments remain clean for a long time. Siopor® clothing can be washed in washing machines.
Maximum comfort. Particles of sweat are transported outside from beneath the garments. It happens with the presence of energy difference beneath the clothes and outside.
Light, comfortable and durable. Siopor® is extremely light, comfortable and very durable – it is a perfect material for work clothes.
Colours. Siopor is available in a wide range of colours.
Washing instructions. Washing temperature: 40°C, chlorination: do not chlorinate, ironing - do not iron, dry cleaning - do not dry clean, drying in clothes dryer – do not dry in drying machines.




TEXOFLEX

It has a one-sided PVC coating on a knitted fabric. This material is resistant to water and wind, elastic and exceptionally durable and weighs 380g/m².
Washing: wash at 40°C, chlorine: do not use chlorine, ironing: do not iron, dry cleaning: do not dry clean, drying: do not dry.





NYLTEX
Unusually light material for general use in industry and sports. Despite its low weight (around 120g/m²) it protects against cold and is perfect for winter clothing. Nylon or polyester on the inside coated with polyurethane.
Washing: wash at 40°C, chlorine: do not use chlorine, ironing: up to 110 °C, dry cleaning: do not dry clean, drying: do not dry.





DUOTEX
Durable material coated on both sides with polyester (around 300g/m²).
Washing: hand wash, chlorine: do not use chlorine, ironing: do not iron, dry clearing: do not dry clean, drying: do not dry.





CHEMFLEX

It features a PVC layer on a knitted fabric. It is coated on one side. It is resistant to water and wind, elastic, unusually durable and weighs 390g/m². It provides protection against some chemicals.
Washing: wash at 30 °C, chlorine: do not use chlorine, ironing: do not iron, dry cleaning: do not dry clean, drying: do not dry.





CHEMTEX

Coated on both sides material (around 360g/m²) which protects against some chemicals.
Washing: hand wash, chlorine: do not use chlorine, ironing: do not iron, dry cleaning: do not dry clean, drying: do not dry.





NICEWEAR vs Traditional clothes
System of replaceable linings
If you want to adjust your clothes to new weather conditions, we prepared a perfect solution for you. You can choose a lining which best suits you needs. The lining is attached to the jacket with a zipper and snap fasteners on the sleeves. This way, your jacket is multifunctional and suitable for all seasons.
3 layers concept
SIOEN concept of multiple layers refers to the use of multiple interactive layers of clothing - each with its specific function..
Basic layer. Also known as absorbing and dispersive layer. Its principal function is to keep the user warm and at the same time ensure that the skin remains dry.
Thermal layer. Thermal layer constitutes an insulation barrier. It is the zone between the basic layer and outer layer, which keeps warmth inside.
Protective layer. It provides protection against all weather conditions such as wind, rain, snow preventing condensation underneath the clothes thanks to its breathability properties.
SIO-FIT
Clothing with Sio-fit fibers provides additional fire protection.
The structure of the fiber provides fire protection within its own molecular structure.This brings the following benefits:
- fire resistance,
- fire resistant properties are not affected by washing,
- optimum parameters guarantee that there will be no melted drops which could cause injuries,
- no need to use chemical agents,
- no impregnation procedure is required,
- it wicks sweat away.
SIO-FIT T-SHIRTS AND POLO SHIRTS
SIO-FIT products include T-shirts and polo shirts of different quality levels. The three lines are: ULTRA LINE, COMFORT LINE AND BASIC LINE.
ULTRA LINE
Comfortable reflective T-shirts and polo shirts made of polyester and rayon. Rayon used on the inner surface absorbs sweat and the reflective polyester surface wicks the sweat away. This ensures optimum control of body temperature.
COMFORT LINE
A combination of polyester and rayon provides excellent protection. The sweat is absorbed and wicked away which ensures that the skin can breathe. The fabric does not cling to the body and controls body temperature regardless of the outside conditions. Comfort Line includes products which are extremely soft and ensure great comfort thanks to drop needles technology.
BASIC LINE
This line of products includes reflective T-shirts and polo shirts. They are made of 100% polyester and feature reflective straps to ensure better visibility. They are light, durable and comfortable. They control sweating and can be machine washed - these are only some of the advantages of these products.
WHY SIO-FIT?
In case of some professions national laws require workers to wear reflective protective clothing approved by CE regardless of the weather conditions. Garments covered by EN471 standard can be uncomfortable in the summer which may provoke thermal shock. The body is overheated.
During manual labour workers produce sweat which is absorbed by their clothes. When they become less active, the body loses the heat and moisture evaporates from their clothing. The body is cooled.
Reflective SIO-FIT polo shirts and T-shirts are an ideal solution to the above problem.
NICEWEAR
NICEWEAR is an ideal solution for those who work in a cold store designed thanks to years of experience and tests. NICEWEAR combines two high-tech materials:
Outer fabric: 55% polyamide / 45% soft cotton with high resistance to abrasion.
Lining: ISOSOFT Thermal structure with unusually small fibers of high-quality polyester which guarantee maximum insulation at a minimum thickness of the fabric.
NICEWEAR maintains its technical and insulating properties even after multiple washing cycles.
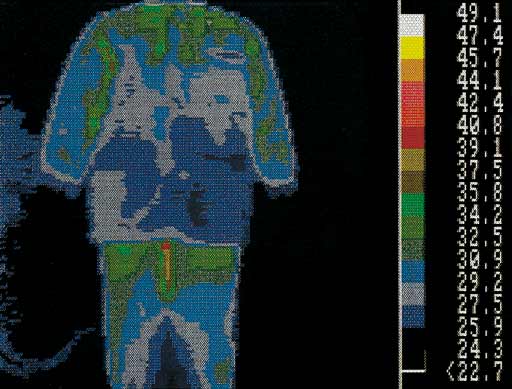
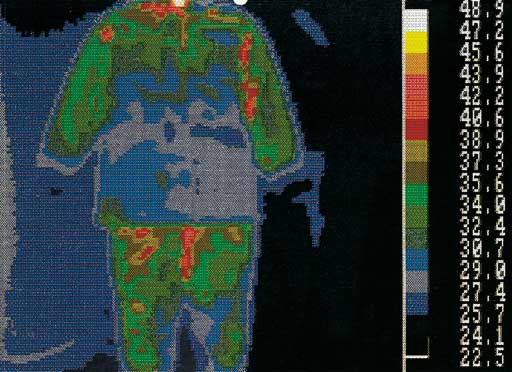
Cold store clothing
We test the properties of NICEWEAR clothing with the use of infrared thermographic scans. In red, areas which are not provided with proper insulation (heat loss) are indicated. In blue, areas with proper insulation (no heat loss) are shown.
In case of conventional cold store clothing with a polyester and cotton lining heat loss occurs in all key areas. NICEWEAR clothing for cold store workers obtained very good results in the test, the body maintains its heat which does not escape from underneath the clothes.
Sio-Cool® fabric
fabric
Breathable reflective strips
SIO SAFE
What is an electric arc?
Electric arc produces and ongoing discharge which is manifested by visible light emission and emission of a large amount of heat. The arc may occur in the space between two electrodes at a low atmospheric pressure (inside and outside). Depending on the intensity the occurrence of arc involves temperatures of up to 10000°C. Moreover, electric arc generates a shock wave which may produce metal and chemical splashes and/or fumes.
Sio-safe benefits:
- Protection against electric arc according to IEC 61482 – Class 2+ Extended Cenelec – lack of second degree injuries (Stoll curve).
- Breathable fabric EN343 – class 3.
- 100% waterproof EN343 – class 3 – waterproof membrane in the outer fabric ensures no water absorption between clothing layers.
- Easy maintenance.
- Thanks to Core-Conductor fibers the material has anti-static properties (lack of surface conductivity).
- Ergonomic clothing. A guarantee of comfort.
- Fire retardant clothing which protects against high temperatures.
New concept - SIO-COOL
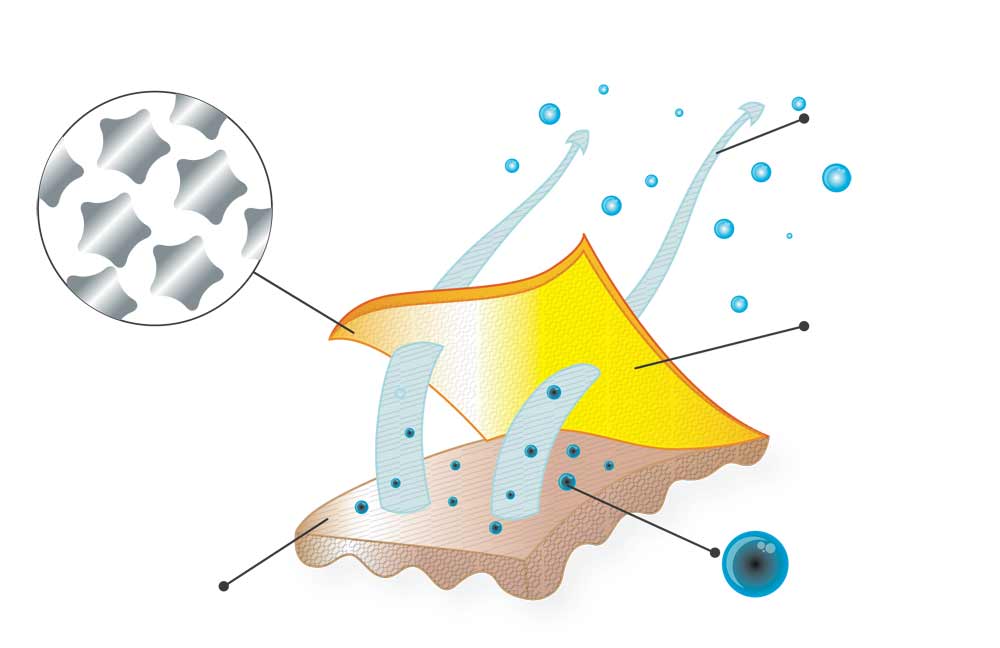
Sio-Cool is a new concept of multifunctional yarn whose parameters ensure that the clothing dries quickly, has antibacterial properties and prevents unpleasant smells. Sio-Cool combines the softness of cotton with polyester features which facilitates maintenance and ensures that the users feel fresh and cool. Excellent design enables transportation of moisture which does not cause loss of dryness or comfort. Sio-Cool does not accumulate sweat but lets it outside. The skin remains dry.
ANTIBACTERIAL PROPERTIES
Incorporation of silver particles (Ag) in the fabric allows Sio-cool to eliminate resistant MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus). It is a bacterium responsible for some complex difficult-to-treat infections. The clothing remains fresh and the smell which the bacteria could produce is eliminated. Silver is not harmful to the body and the antibacterial properties are permanent.
ABSORBS AND DRIES QUICKLY
The clothing contains numerous channels which move moisture away from the skin in the upper layer of the fabric.
DUPONT PERSONAL PROTECTION®
Cleanliness class on target markets
| ISO | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FS 209 | - | - | 1 | 10 | 100 | 1000 | 10000 | 100000 | - | ||||||||||
| GMP | - | - | - | - | A/B | - | C | D | - | ||||||||||
Electronics industry | |||||||||||||||||||
Pharmaceutical industry | |||||||||||||||||||
Food industry | |||||||||||||||||||
Health care industry | |||||||||||||||||||
Ophthalmic industry | |||||||||||||||||||
Aircraft industry | |||||||||||||||||||
Automotive industry | |||||||||||||||||||
protective suits - Cleanroom
Some of the DuPont® suits are suitable for use in cleanroom applications.
Cleanroom is an area with a system of controlling contamination with particles or microbes designed and used in such a way as to prevent entering, creating and accumulating impurities.
Such areas are designed for the purposes of research and production processes which involve the use of high purity materials (e.g. central processing units).
Cleanroom classification
Cleanrooms are classified according to the required atmosphere purity into classes which specify the number and volume of permitted particles per cubic metre (or cubic foot) of air.
Properties and application of the suits
Classification of number of particles by cleanliness class according to applicable standards:
| Rozp. MZ/cGMP | SI Fed.Std.209e | Ang. Fed.Std. 209d | PN-EN ISO 14644-1:2005 | Maximum permitted number of particles per m³ with size equal to or greater than that specified | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0,1µm | 0,2µm | 0,3µm | 0,5µm | 1,0µm | 5,0µm | ||||
| ISO Class1 | 10 | 2 | - | - | - | - | |||
| ISO Class2 | 100 | 24 | 10 | 4 | - | - | |||
| M1 | 350 | 75,5 | 30,9 | 10 | - | ||||
| ISO Class3 | 1000 | 237 | 102 | 35 | 8 | - | |||
| M 1,5 | | | 1240 | 265 | 106 | 35.3 | ||||
| M2 | 3.500 | 757 | 308 | 100 | - | ||||
| ISO Class4 | 10.000 | 2.370 | 1.020 | 352 | 83 | - | |||
| M 2,5 | 10 | 12.400 | 2.650 | 1.060 | 353 | - | |||
| M3 | 35.000 | 7.570 | 3.090 | 1.000 | - | ||||
| A / B | 3.500 | 1 | |||||||
| ISO Class5 | 100.000 | 23.700 | 10.200 | 3.520 | 832 | 29 | |||
| M 3,5 | 100 | 26.500 | 10.600 | 3.530 | - | ||||
| M4 | 75.700 | 30.900 | 10.000 | - | |||||
| ISO Class6 | 1.000.000 | 237.000 | 102.000 | 35.200 | 8.320 | 293 | |||
| M 4,5 | 1000 | 35.300 | 247 | ||||||
| M5 | 100.000 | 618 | |||||||
| C | 350.00.0 | 2.000 | |||||||
| ISO Class7 | 352.000 | 83.200 | 2.930 | ||||||
| M 5,5 | 10.000 | 353.000 | 1 | 2.470 | |||||
| M6 | 1.000.000 | 6.180 | |||||||
| D | 3.500.000 | 20.000 | |||||||
| ISO Class8 | 3.520.000 | 832.000 | 29.300 | ||||||
| M 6,5 | 100.000 | 3.530.000 | 24.700 | ||||||
| M7 | 10.000.000 | 61.800 | |||||||
| ISO Class9 | 35.200.000 | 8.320.000 | 293.000 | ||||||

TYCHEM® TK
The fabric, eye protection, zipper and seams are an excellent barrier. The suit is easy to put on and take off and comfortable - the material is very elastic and easily bent. Large and carefully designed eye protection screen ensures high visibility. The suit is lightweight - it weighs around 2kg.
Application: medical rescue, firefighting.
It complies with the following standards:



TYCHEM® F
It provides protection against organic chemical substances, concentrated inorganic chemical substances and biological agents. It resists liquid splashes of pressures up to 5 bar.
Application: chemical industry, pharmaceutics, removing hazardous materials, contact with agricultural chemicals, medical rescue.
It complies with the following standards:









TYCHEM® C
It provides protection against concentrated inorganic chemical substances and biological agents. It resists liquid splashes of pressures up to 2 bar.
Application: chemical industry, pharmaceutics, removing hazardous materials, contact with agricultural chemicals, medical rescue.
It complies with the following standards:









TYVEK® Classic Xpert
Tyvek® Classic Xpert provides maximum protection against liquids, solid particles and biological agents. The suit features high-tech seams which are a more effective barrier than traditional seams. Tyvek® nonwoven fabric does not emit dust or absorb liquids. Solid particles do not cling to the fabric. It is suitable for use in cleanroom applications.
Application: varnishing, chemical industry, pharmaceutics, cleaning and maintenance work in industrial plants, food processing.
It complies with the following standards:






TYVEK® Classic PLUS
TYVEK® Classic Plus prevents liquid penetration and provides excellent protection against toxic solid particles and biological hazards thanks to specialist tight taped seams. It is suitable for use in cleanroom applications.
Application: varnishing, chemical industry, pharmaceutics, cleaning and maintenance work in industrial plants, food processing.
It complies with the following standards:







TYVEK® Labo
It protects both the user and the production process against contamination. Tyvek® Labo features an anti-static finish on both sides of the fabric and shoe protectors connected with suit legs. It is suitable for use in cleanroom applications.
Application: laboratories, pharmaceutics, microelectronics.
It complies with the following standards:






TYVEK® Dual
The front of the suit is made of Tyvek® nonwoven fabric which protects against splashes of liquid chemicals and solid particles. The back, from the ankles to the head, is made of breathable fabric manufactured according to patented ACT technology (Advanced Composite Technology) and demonstrates high air and vapour permeability.
Application: boat building, production of wind farm elements (blades, heads), food industry (bakeries), glass production, production of building materials (brick firing).
It complies with the following standards:






PROSHIELD® Comfort 10
PROSHIELD® Comfort 10 protective suit reduces the risk of overheating during intensive work or working in high temperatures and reduces sweating. It is very comfortable, light and offers a nice feel and freedom of moves (ample crotch area).
Application: the suit is perfect for work which does not require a very high degree of protection but a maximum comfort of the user: glass or rubber production, brick or ceramic firing, spray painting, casting and smelting.
It complies with the following standards:






EASYSAFE®
EASYSAFE® protective suit
It is made of a new polyethylene nonwoven fabric whose structure is more open than the structure of Tyvek®. The suit is more durable and breathable than suits made of microporous film. It provides a higher degree of protection than suits made of SMS fabrics.
Application: contact with glass fibers, pharmaceutics if there is low exposure to chemical substances, wide range of production industries, industrial repairs and cleaning.
It complies with the following standards:





PROSHIELD® FR
The suit reduces flame spread, it is designed to be worn on incombustible garments. It protects against short-term small flames, small splashes of chemicals, aerosols and solid particles. At the same time it protects reusable incombustible clothing underneath.
Application: petroleum, rail, metallurgy and gas industries.
It complies with the following standards:






Classification of DuPont® coveralls by their intended application
 |  |  |  |  |  |
| Dirt, dust, low concentration of inorganic compounds | Concentrated inorganic compounds | Organic compounds, highly concentrated inorganic compounds | Gases, toxic solids | ||
Najprawdopodobniej wystąpił błąd. Wygląda na to, że twoja przeglądarka nie spełnia standardów wymaganych przez tą aplikację. Prosimy o aktualizację do nowszej wersji lub użycie innej przeglądarki!
Kompatybilne wersje przeglądarek: Internet Explorer 9+, Mozilla Firefox 24+, Google Chrome 29+, Opera 21+ oraz inne nowoczesne przeglądarki wspierające technologię HTML5.
Zalecamy korzystanie zawsze z najnowszych, w pełni zaktualizowanych wersji przeglądarek!
Nie masz zgodnej przeglądarki? Poniżej znajdziesz linki do instalatorów najbardziej popularnych i zalecanych przeglądarek:
pobierz Mozilla Firefox pobierz Google Chrome pobierz Opera
There was an error. Most likely, your browser does not meet the standards required by the application. Please upgrade to a newer version or use a different browser!
Compatible browsers: Internet Explorer 9 +, Mozilla Firefox 24 +, Chrome 29 +, Opera 21 + and other modern browsers support HTML5 technology.
We recommend that you always use the latest, fully updated versions of supported browsers!
No compatible browser? Below you will find links to the installers of the most popular and recommended browsers:
download Mozilla Firefox download Google Chrome download Opera
Произошла ошибка. Скорее всего, ваш браузер не соответствует стандартам, требуемым приложением. Обновите версию до новой версии или используйте другой браузер!
Совместимые браузеры: Internet Explorer 9 +, Mozilla Firefox 24 +, Chrome 29 +, Opera 21 + и другие современные браузеры поддерживают технологию HTML5.
Мы рекомендуем всегда использовать новейшие, полностью обновленные версии поддерживаемых браузеров!
Совместимый браузер отсутствует Ниже вы найдете ссылки на инсталляторы самых популярных и рекомендуемых браузеров:
загрузить Mozilla Firefox загрузить Google Chrome загрузить Opera
Es ist ein Fehler aufgetreten . Höchstwahrscheinlich entspricht Ihr Browser nicht den von der Anwendung geforderten Standards. Bitte aktualisieren Sie auf eine neuere Version oder verwenden Sie einen anderen Browser!
Kompatible Browser: Internet Explorer 9 +, Mozilla Firefox 24 +, Chrome 29 +, Opera 21+ und andere moderne Browser unterstützen die HTML5-Technologie.
Wir empfehlen, immer die neuesten, vollständig aktualisierten Versionen der unterstützten Browser zu verwenden!
Kein kompatibler Browser? Unten finden Sie Links zu den Installern der beliebtesten und empfohlenen Browser:
Mozilla Firefox herunterladen Google Chrome herunterladen Opera herunterladen
( Niezalecane, chyba, że jesteś pewna/pewien, że twoja przeglądarka spełnia wymagane standardy / Not recommended unless you are certain that the web browser meets the required standards / Не рекомендуется, если вы не уверены, что веб-браузер соответствует требуемым стандартам / Nicht empfohlen, es sei denn, Sie sind sicher, dass der Webbrowser die erforderlichen Standards erfüllt )